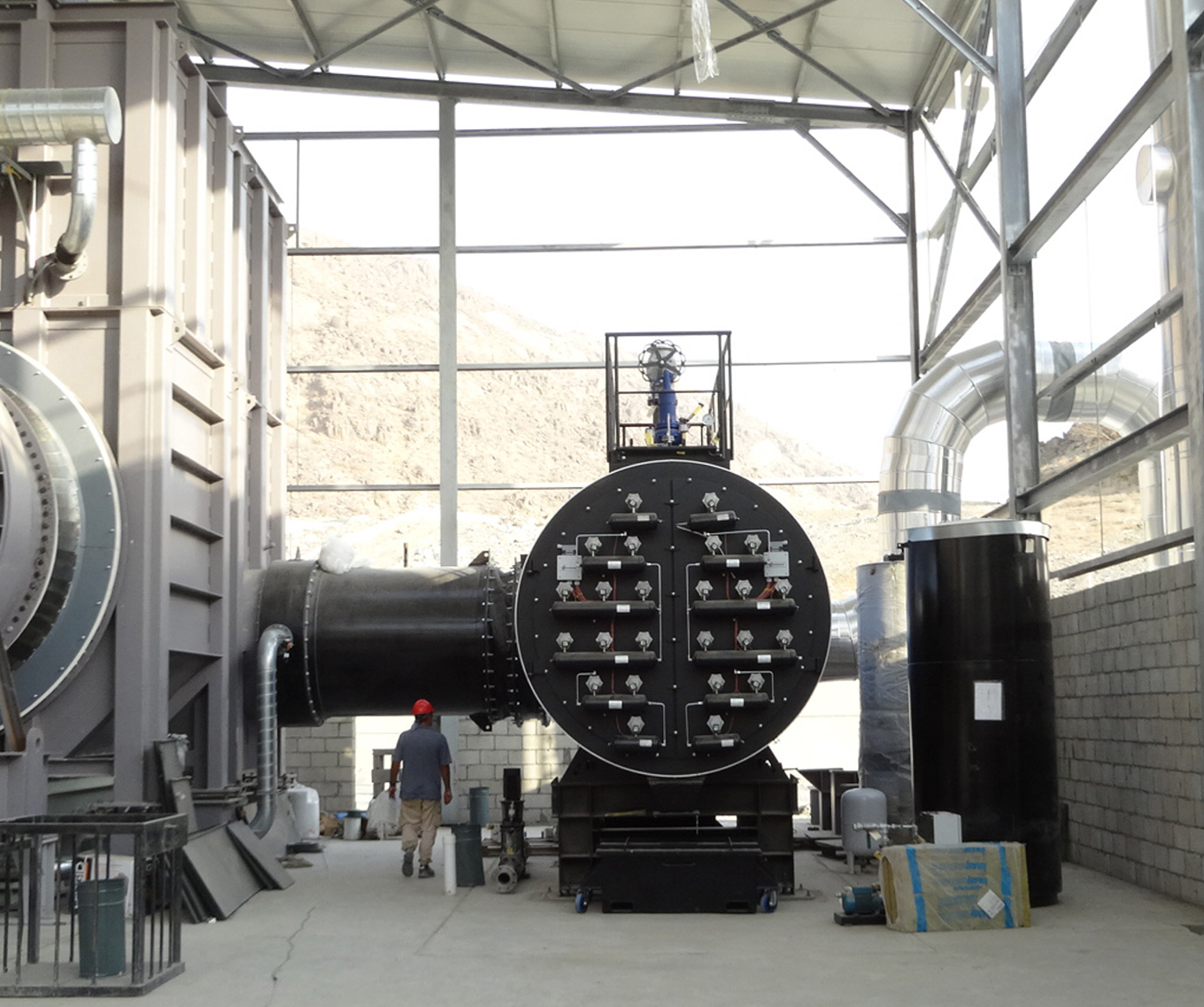
In contrast, waste-to-energy incineration plants utilize advanced technologies to convert waste into energy. The process involves controlled combustion of waste materials, such as municipal solid, industrial, or agricultural waste, in specially designed chambers. This combustion process not only reduces the volume of waste but also harnesses the energy released during the process.
By converting waste into energy, these incineration plants offer a cleaner alternative to traditional forms of energy generation. The combustion process is carried out under strict environmental regulations and utilises sophisticated air pollution control systems. These systems capture and treat harmful emissions, such as particulate matter, heavy metals, and dioxins, before they are released into the atmosphere.
COME INIZIARE
Hot Water
Advantages
Hot water energy recovery reduces greenhouse gas emissions and is cost-effective with low capital investment. It's simple integration into existing systems ensures minimal disruption and facilitates widespread adoption.
Learn MoreSteam
Advantages
Steam energy recovery systems provide substantial carbon offsets by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing the overall efficiency of energy use. Their high recovery efficiencies translate to better performance and greater energy savings.
Learn MoreElectricity
Advantages
Electricity energy recovery contributes to significant carbon offsets by optimizing energy use and reducing emissions. It also supports the parasitic load of the plant, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability.
Learn MoreHOT WATER
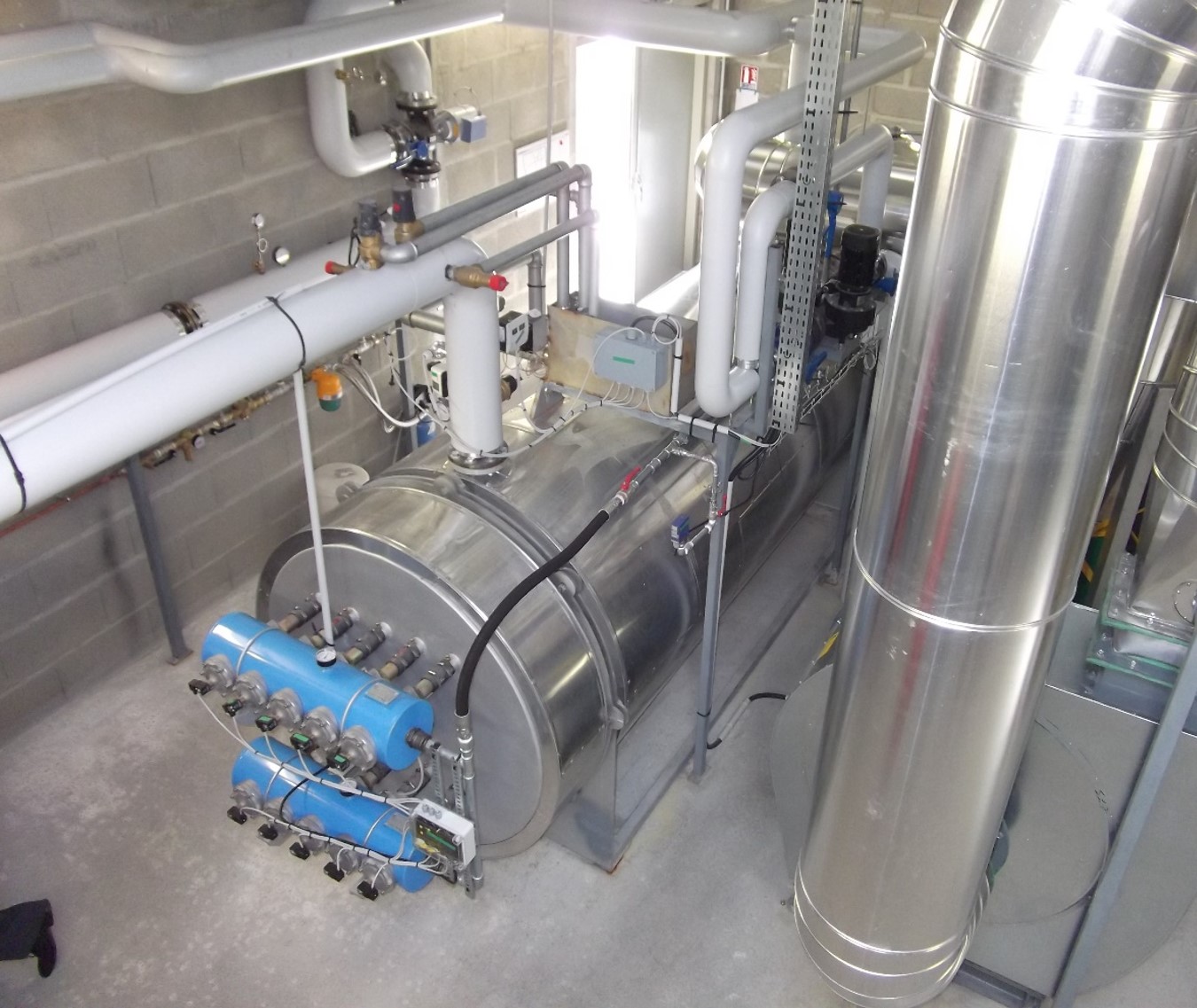
Hot water is a key requirement within many industrial processes or it can be used as a method of generating the heating requirements of any type of building.
Heat is recovered indirectly from incinerator exhaust gases by passing them through a gas tube heat exchanger. Heat is then exchanged with the external water jacket to generate a cost-free supply of hot water.
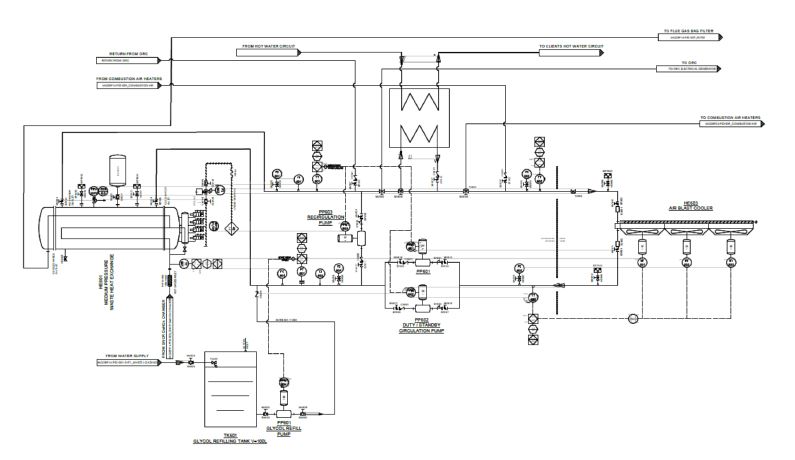

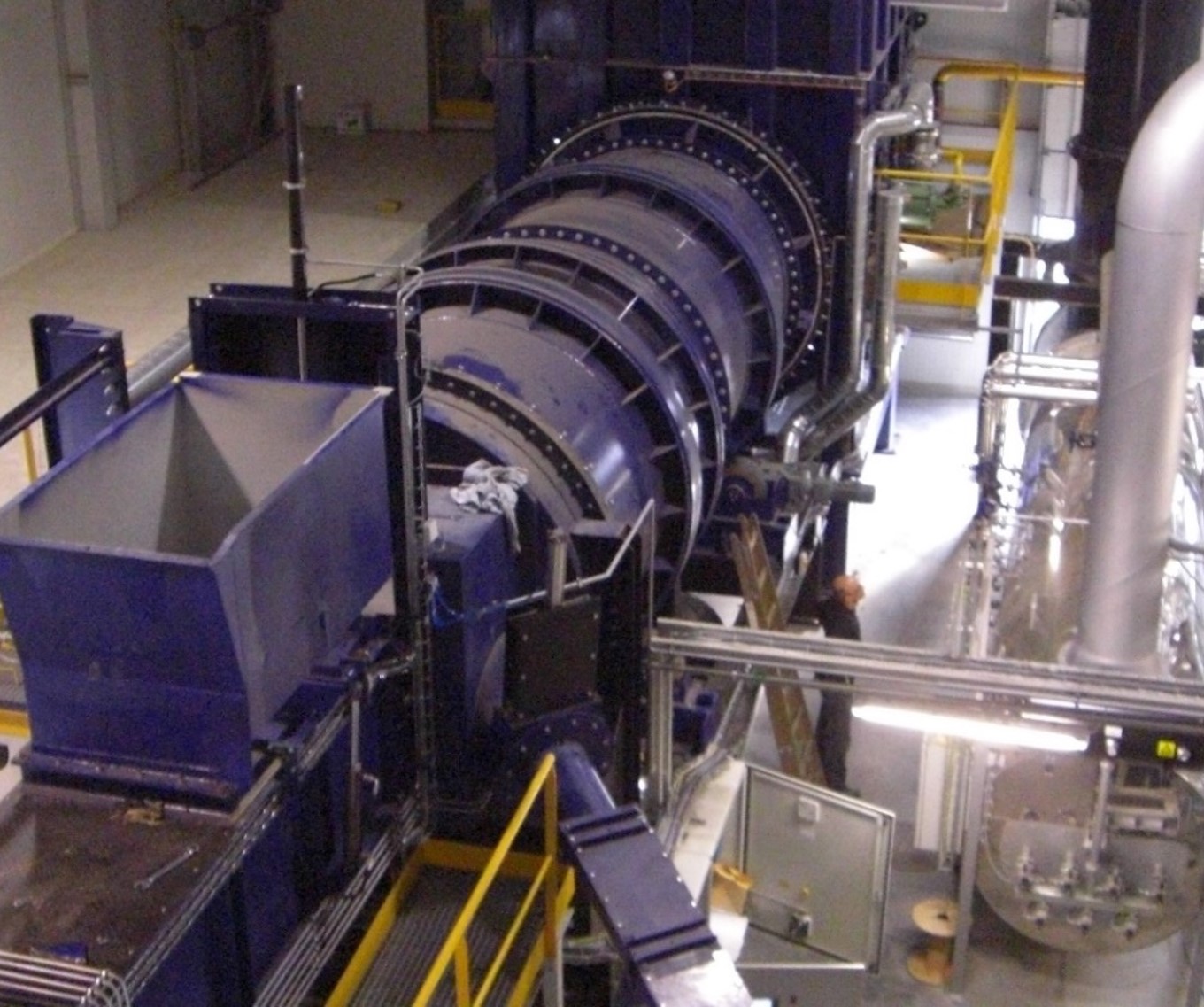
STEAM
Steam has many potential uses including heating for buildings and we can design any pet cremator with the technology to convert what would be waste heat into this valuable resource.
Heat is recovered indirectly from the incinerator exhaust gases by passing them either through a gas tube heat exchanger or across a radiant tube boiler. Energy is exchanged between the gases and water to produce steam.
When the intention is for the steam to be used for Energy Generation such as electrical power production, it is further heated within a superheater to produce dry steam to drive a turbine/generator set.
Economizers are fitted to the boiler outlet to recover additional energy from the flue gas.
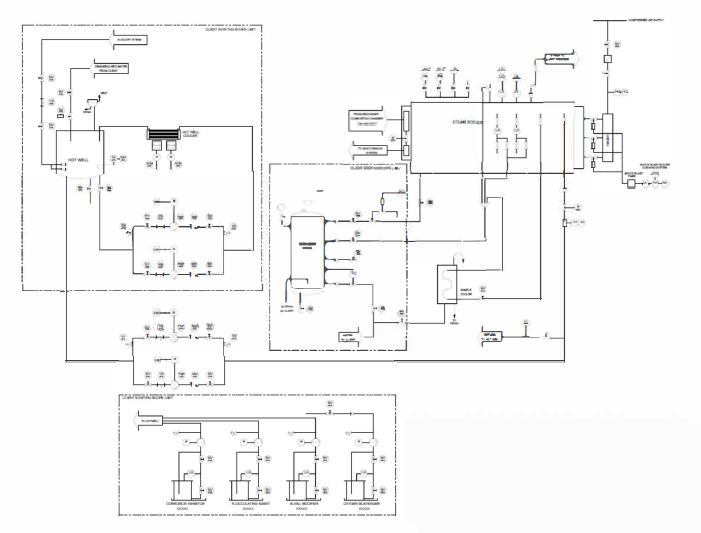

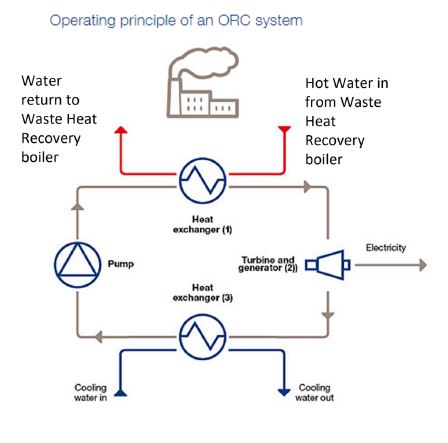
ELECTRICITY
Electricity
This is generated in two forms.
1. Convert the energy in the gas to very high-pressure steam and inject the steam into a turbine and generator set. Cost include such of the turbine, associated plant and grid connection.
2. Pass the gas through an organic rankine cycle generator. This works much the same as a refrigerator. The gas heats a liquid, which superheats, expands and spins a small turbine. These are much less complicated and are more compact than a high-pressure turbine system but are less efficient. These are typically used to provide circa 50kW of electrical power to compliment the parasitic load of the process or building.